Lvalues and Rvalues
对于刚学习 C++ 的同学来说,可能会经常遇见过这样的错误: The left operand must be an lvalue (C2106)。 这句话的意思是,左操作数必须为 lvalue。
大家可能只听过 lvalue 和 rvalue,但是并不知道它们到底是什么,因为传统 C++ 也不需要过多的了解。但是在现代 C++ 中,知道这些概念(特别是 rvalue reference)可以有效地提升程序的内存效率,下面看一下它们具体的定义吧。
lvalue and rvalue
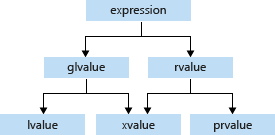
- A glvalue is an expression whose evaluation determines the identity of an object, bit-field, or function.
- A prvalue is an expression whose evaluation initializes an object or a bit-field, or computes the value of the operand of an operator, as specified by the context in which it appears.
- An xvalue is a glvalue that denotes an object or bit-field whose resources can be reused (usually because it is near the end of its lifetime). Example: Certain kinds of expressions involving rvalue references (8.3.2) yield xvalues, such as a call to a function whose return type is an rvalue reference or a cast to an rvalue reference type.
- An lvalue is a glvalue that is not an xvalue.
- An rvalue is a prvalue or an xvalue.
它们的关系如下:
An lvalue has an address that your program can access. Examples of lvalue expressions include variable names, including const variables, array elements, function calls that return an lvalue reference, bit-fields, unions, and class members.
A prvalue expression has no address that is accessible by your program. Examples of prvalue expressions include literals, function calls that return a non-reference type, and temporary objects that are created during expression evaluation but accessible only by the compiler.
An xvalue expression has an address that no longer accessible by your program but can be used to initialize an rvalue reference, which provides access to the expression. Examples include function calls that return an rvalue reference, and the array subscript, member and pointer to member expressions where the array or object is an rvalue reference.
example
// lvalues_and_rvalues2.cppint main(){int i, j, *p;// Correct usage: the variable i is an lvalue and the literal 7 is a prvalue.i = 7;// Incorrect usage: The left operand must be an lvalue (C2106).`j * 4` is a prvalue.7 = i; // C2106j * 4 = 7; // C2106// Correct usage: the dereferenced pointer is an lvalue.*p = i;// Correct usage: the conditional operator returns an lvalue.((i < 3) ? i : j) = 7;// Incorrect usage: the constant ci is a non-modifiable lvalue (C3892).const int ci = 7;ci = 9; // C3892}
lvalue reference and rvalue reference
这部分可以看这个地址的介绍: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/cpp/cpp/references-cpp?view=msvc-170
里面除了介绍 lvalue reference 和 rvalue reference,也提到和 reference 和 pointer 的对比。